| |
|
|
|
(Y. Sohma, et al. Chem. Commun. 2004, 124-5; M. Mutter, et al. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 4172-8; L.A. Carpino, et al. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 7519-23; S.D. Santos, et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 11888-9)
(Y. Sohma, et al. Chem. Commun. 2004, 124-5; Y. Sohma, et al. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 5965-8; Y. Sohma, et al. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 13, 6167-74; Y. Sohma, et al. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 3013-7.)
(Y. Sohma, et al. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 3013-7; T. Yoshiya, et al. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 1720-30)
(J. Coin, et al. Nature Protocols 2007, 2, 3247-56.)
(T. Yoshiya, et al. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 7095-9)
|
|
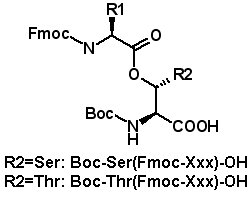
Isoacyl Dipeptides |
 |
| |
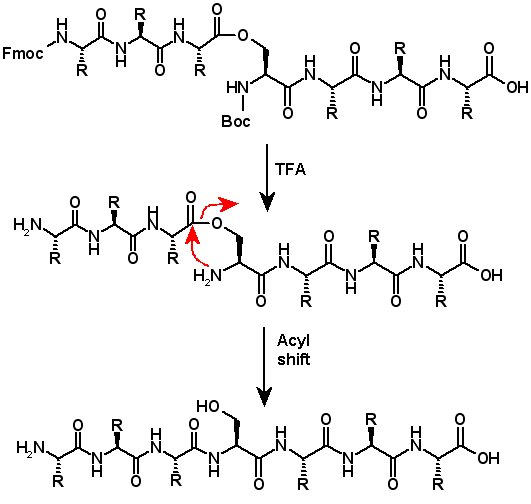
Isoacyl dipeptides consist of an Fmoc-protected amino acid attached to the alcohol side chain of Boc-serine or Boc-threonine. The isoacyl dipeptides undergo O → N acyl shift when the Boc protecting group is removed and the pH is adjusted to 7.4 or higher (Y. Sohma, et al. Chem. Commun. 2004, 124-5; M. Mutter, et al. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 4172-8; L.A. Carpino, et al. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 7519-23; S.D. Santos, et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 11888-9). Isoacyl peptides can be utilized with ordinary Fmoc protocols to prepare isoacyl peptides. Isoacyl dipeptides are less prone to aggregation since the regular pattern of hydrogen bonding in the peptide chain is disrupted. Isoacyl peptides are very soluble and are often more soluble than their native peptide counterparts. Therefore it is often easier to purify and isolate the peptide product when it is an isoacyl intermediate, then perform the acyl shifts to produce the pure native peptide.(Y. Sohma, et al. Chem. Commun. 2004, 124-5; Y. Sohma, et al. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 5965-8; Y. Sohma, et al. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 13, 6167-74; Y. Sohma, et al. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 3013-7.) |
|
| |
 |
|
| |
Isoacyl dipeptides can be formed on resin, but the conditions required for coupling can produce significant levels of racemization in the acyl amino acid. Isoacyl dipeptides can be formed in solution phase, however, nearly racemization-free (Y. Sohma, et al. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 3013-7; T. Yoshiya, et al. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 1720-30). Thus to avoid racemization, isoacyl peptides are synthesized utilizing preformed isoacyl dipeptides to introduce the isoacyl peptide bond, followed by conventional solid phase peptide synthesis protocols. Diketopiperazine formation has been reported in some instances, but this can be prevented by using Bsmoc-protected amino acids for the first coupling onto isoacyl peptides.(J. Coin, et al. Nature Protocols 2007, 2, 3247-56.)
Isoacyl dipeptides are also useful tools for segment condensation. Incorporated as the C-terminus of the N-segment, isoacyl dipeptides allow peptide segments to be coupled with very little racemization of the activated amino acid residue. After forming the isopeptide by segment coupling, rearrangement through the acyl shift results in the desired peptide. (T. Yoshiya, et al. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 7095-9). |
|
| AAPPTec Isoacyl Dipeptides |
| |
Catalog # |
Isoacyl Dipeptide |
| |
IAD001 |
Boc-Ser(Fmoc-Ala)-OH |
| |
IAD002 |
Boc-Thr(Fmoc-Ala)-OH |
| |
IAD003 |
Boc-Ser[Fmoc-Asn(Trt)]-OH |
| |
IAD004 |
Boc-Thr[Fmoc-Asn(Trt)]-OH |
| |
IAD005 |
Boc-Ser[Fmoc-Asp(OtBu)]-OH |
| |
IAD006 |
Boc-Thr[Fmoc-Asp(OtBu)]-OH |
| |
IAD007 |
Boc-Ser[Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)]-OH |
| |
IAD008 |
Boc-Thr[Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)])-OH |
| |
IAD009 |
Boc-Ser[Fmoc-Gln(Trt)]-OH |
| |
IAD010 |
Boc-Thr[Fmoc-Gln(Trt)]-OH |
| |
IAD011 |
Boc-Ser[Fmoc-Glu(OtBu)]-OH |
| |
IAD012 |
Boc-Thr[Fmoc-Glu(OtBu)]-OH |
| |
IAD013 |
Boc-Ser(Fmoc-Gly)-OH |
| |
IAD014 |
Boc-Thr(Fmoc-Gly)-OH |
| |
IAD015 |
Boc-Ser[Fmoc-His(Trt)]-OH |
| |
IAD016 |
Boc-Thr[Fmoc-His(Trt)]-OH |
| |
IAD017 |
Boc-Ser(Fmoc-Ile)-OH |
| |
IAD018 |
Boc-Thr(Fmoc-Ile)-OH |
| |
IAD019 |
Boc-Ser(Fmoc-Leu)-OH |
| |
IAD020 |
Boc-Thr(Fmoc-Leu)-OH |
| |
IAD021 |
Boc-Ser[Fmoc-Lys(Boc)]-OH |
| |
IAD022 |
Boc-Thr[Fmoc-Lys(Boc)]-OH |
| |
IAD023 |
Boc-Ser(Fmoc-Met)-OH |
| |
IAD024 |
Boc-Thr(Fmoc-Met)-OH |
| |
IAD025 |
Boc-Ser(Fmoc-Phe)-OH |
| |
IAD026 |
Boc-Thr(Fmoc-Phe)-OH |
| |
IAD027 |
Boc-Ser[Fmoc-Ser(tBu)]-OH |
| |
IAD028 |
Boc-Thr[Fmoc-Ser(tBu)]-OH |
| |
IAD029 |
Boc-Ser[Fmoc-Thr(tBu)]-OH |
| |
IAD030 |
Boc-Ser[Fmoc-Trp(Boc)]-OH |
| |
IAD031 |
Boc-Thr[Fmoc-Trp(Boc)]-OH |
| |
IAD032 |
Boc-Ser[Fmoc-Tyr(tBu)]-OH |
| |
IAD033 |
Boc-Thr[Fmoc-Tyr(tBu)]-OH |
| |
IAD034 |
Boc-Ser(Fmoc-Val)-OH |
| |
IAD035 |
Boc-Thr(Fmoc-Val)-OH |
|
| |



